All About Amino Acids
Learn More
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein, and protein is essential for nearly every part of the body — from muscle and connective tissue to skin, nails, blood, and vital organs.
Full Body Impact delivers all 20 amino acids, including the 9 essential ones your body cannot produce on its own. Each plays a unique role in supporting strength, recovery, and overall health.
Below, you’ll find a breakdown of the amino acids in our collagen, along with their key benefits.
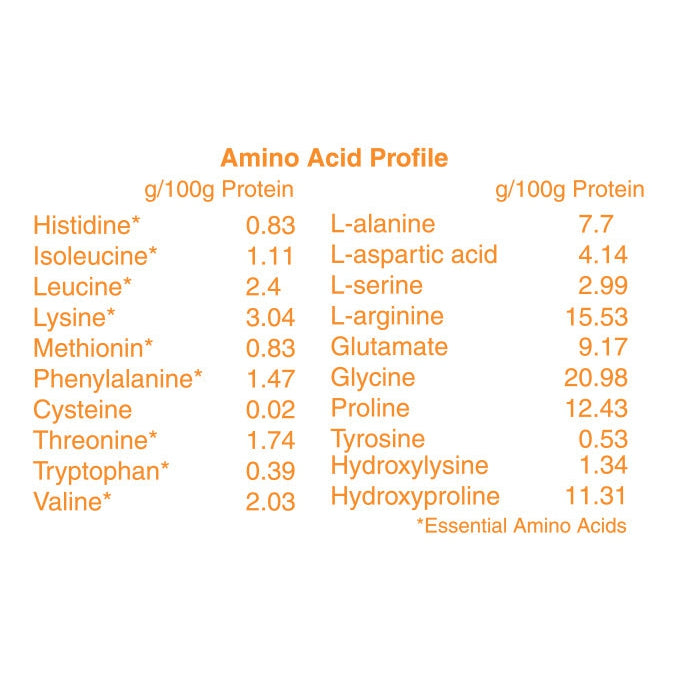
Our Amino Acid Breakdown
Histidine
Supports growth and tissue repair, helps make blood cells, protects nerve cells, and is used by the body to make histamine.
Isoleucine
Supports hemoglobin production, may help control blood sugar, and boosts energy and endurance.
Leucine (BCAA)
Fuels muscles during exercise, aids skin and bone healing, promotes lean muscle growth, and may help regulate blood sugar.
Lysine
Essential for collagen formation, growth, calcium absorption, and energy production. Plays a key role in connective tissue health.
Methionine
Acts as an antioxidant and may help protect damaged tissues.
Phenylalanine
Supports skin health, helps manage pain, and is linked to weight and mood balance.
Cysteine
Precursor to glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that helps fight free radicals and slow aging.
Threonine
Builds collagen and elastin, supports muscle growth, and helps regulate mood and digestion.
Tryptophan
Essential for protein, enzyme, and neurotransmitter production. Supports muscle and brain health.
Valine (BCAA)
Supports muscle growth, energy, and hydration. Important for mental focus, coordination, and calm.
Alanine
Balances skin hydration, provides energy to muscles and the nervous system, and supports immune health.
Aspartate
Enhances mineral absorption, supports athletic performance, and helps protect skin against aging.
Serine
Critical for protein and muscle production, fat metabolism, and antibody creation. Also a natural skin moisturizer.
Arginine
Hydrates skin, reduces fine lines and wrinkles, supports circulation, and helps build protein. Converts to nitric oxide for improved blood flow.
Glutamate
Key in protein and energy metabolism, helps reconstruct body proteins.
Glycine
Supports cell growth, antioxidant production, and fights oxidative stress that damages skin and tissues.
Proline
Important for protein structure, wound healing, antioxidative reactions, and immune health.
Tyrosine
Helps produce melanin, supporting skin tone and protection.
Hydroxyproline
Protects collagen and elastin, often used for its anti-aging benefits.
Hydroxylysine
Supports bone density and strength.



